Genomic Data Processing with GenomeFlow
Published in BMC Bioinformatics, 2024.
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School
Abstract
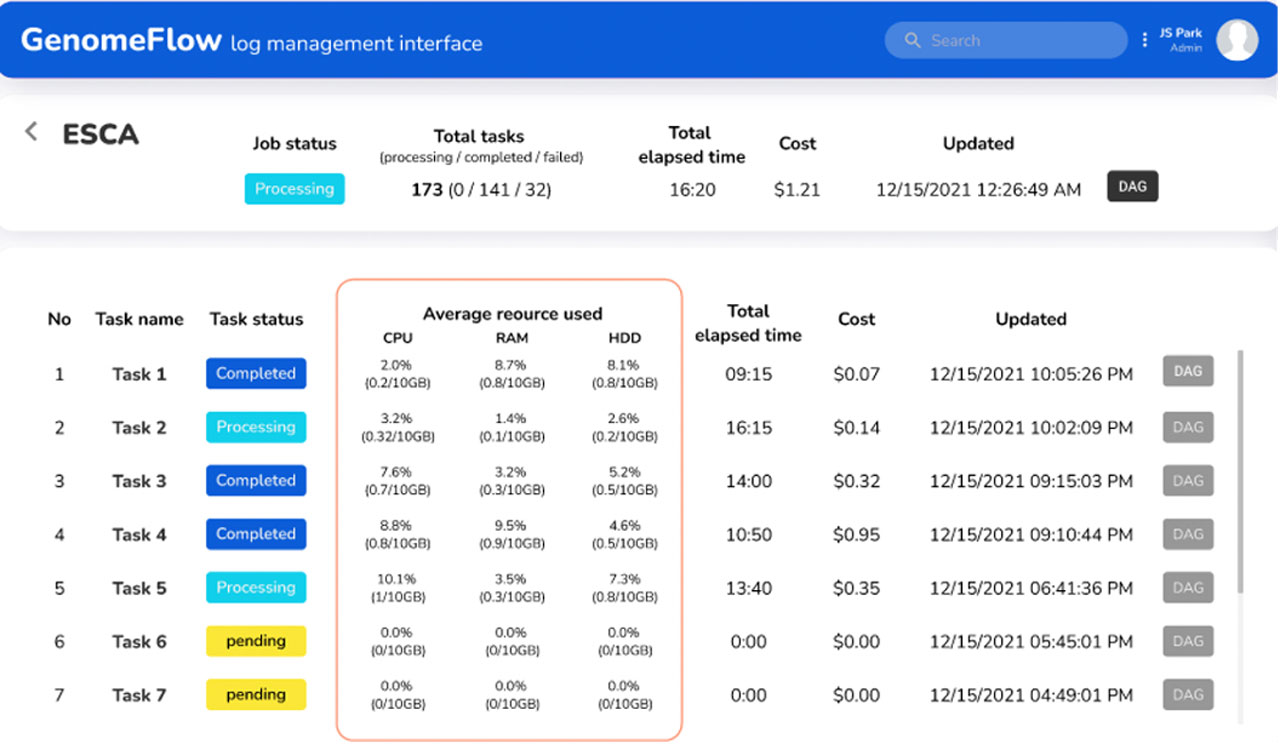
Advances in genome sequencing technologies generate massive amounts of sequence data that are increasingly analyzed and shared through public repositories. On-demand infrastructure services on cloud computing platforms enable the processing of such large-scale genomic sequence data in distributed processing environments with a significant reduction in analysis time. However, parallel processing on cloud computing platforms presents many challenges to researchers, even skillful bioinformaticians. In particular, it is difficult to design a computing architecture optimized to reduce the cost of computing and disk storage as genomic data analysis pipelines often employ many heterogeneous tools with different resource requirements. To address these issues, we developed GenomeFlow, a tool for automated development of computing architecture and resource optimization on Google Cloud Platform, which allows users to process a large number of samples at minimal cost. We outline multiple use cases of GenomeFlow demonstrating its utility to significantly reduce computing time and cost associated with analyzing genomic and transcriptomic data from hundreds to tens of thousands of samples from several consortia. Here, we describe a step-by-step protocol on how to use GenomeFlow for a common genomic data processing task. We introduce this example protocol geared toward a bioinformatician with little experience in cloud computing.
Materials